Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of our nervous system, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell production. It is primarily found in animal-based foods, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. However, individuals who regularly use proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to manage conditions like acid reflux or GERD may be at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency.
PPIs work by reducing the production of stomach acid, which can provide relief from heartburn and other acid-related symptoms. However, long-term use of PPIs can interfere with the absorption of certain nutrients, including vitamin B12. This can lead to a deficiency, which can have serious health implications.
The Role of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is involved in numerous bodily processes and is essential for overall well-being. Here are some key benefits of vitamin B12:
- Energy Production: Vitamin B12 helps convert the food we eat into energy, supporting optimal metabolism.
- Nervous System Health: It plays a vital role in maintaining the health of our brain and nervous system.
- Red Blood Cell Formation: Vitamin B12 is necessary for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
- DNA Synthesis: It is involved in the synthesis of DNA, the genetic material present in all cells.
- Mood Regulation: Vitamin B12 is believed to play a role in the production of neurotransmitters, which affect mood and mental well-being.
Risk of Vitamin B12 Deficiency in PPI Users
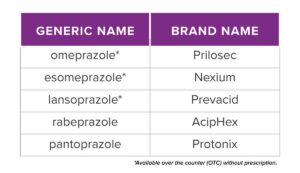
Studies have shown that PPI users have a higher risk of developing vitamin B12 deficiency compared to those who do not use these medications. The reduced stomach acid production caused by PPIs hinders the absorption of vitamin B12 from food.
Common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency include fatigue, weakness, tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty concentrating, and mood disturbances. If left untreated, a deficiency can lead to more severe complications, such as anaemia, nerve damage, and cognitive impairment.
The Importance of Oral Supplementation
If you are regularly taking PPIs, it is crucial to ensure an adequate intake of vitamin B12. One way to do this is through oral supplementation. Taking a vitamin B12 supplement orally can help replenish your body’s stores and prevent deficiency.
When choosing a vitamin B12 supplement, look for methylcobalamin or cyanocobalamin, as these are the most common and well-absorbed forms of the vitamin. It is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage for your needs.
Additionally, incorporating foods rich in vitamin B12 into your diet can also help boost your intake. These include animal-based products like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, consider fortified foods or B12 supplements specifically formulated for those dietary preferences.
Conclusion on Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Individuals who regularly use PPIs may be at risk of vitamin B12 deficiency due to reduced stomach acid production. To prevent deficiency, oral supplementation of vitamin B12 is recommended for PPI users. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and consider incorporating vitamin B12-rich foods into your diet.
